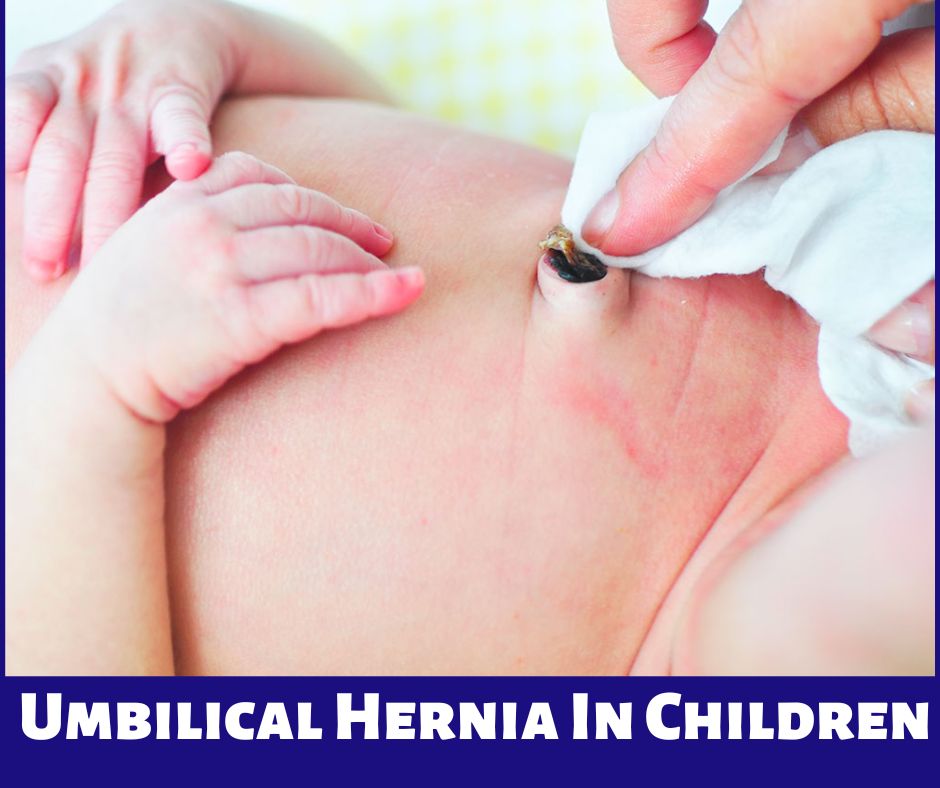
An umbilical hernia is a common condition in infants and young children. It occurs when a portion of the intestine or other abdominal contents bulges through a weakness in the abdominal muscles around the navel or belly button. In this article, we will discuss the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment of umbilical Hernia In Children.
Causes of Umbilical Hernia in Children
Umbilical hernias are typically the result of a congenital weakness in the abdominal muscles. This means that the muscles around the navel did not close properly during fetal development, leaving a small gap or opening that allows the intestine or other abdominal contents to bulge out.
Risk factors for umbilical hernia in children include premature birth, low birth weight, and a family history of hernias. In some cases, umbilical hernias can also be caused by increased abdominal pressure, such as that caused by crying, coughing, or straining during a bowel movement.
Symptoms
The most common symptom of an umbilical hernia in children is a bulge or swelling around the navel. The bulge may be more noticeable when the child is crying, coughing, or straining, and may disappear when the child is relaxed or lying down.
Umbilical hernias in children are usually painless, but they may cause discomfort or mild pain if the contents of the hernia become trapped or twisted. Signs of a trapped hernia include severe pain, redness or discoloration of the bulge, and vomiting.
Diagnosis of Umbilical Hernia in Children
Umbilical hernias in children are usually diagnosed by physical examination. The healthcare provider will examine the child’s abdomen and look for a bulge or swelling around the navel. The provider may also check to see if the hernia is reducible, which means that it can be pushed back into the abdominal cavity. In some cases, imaging tests such as ultrasound may be recommended to confirm the diagnosis or rule out other conditions for Paediatric Hernia Treatment in Goregaon.
Treatment
In most cases, umbilical hernias in children will close on their own as the abdominal muscles strengthen and develop over time. Therefore, observation and monitoring are often recommended for small or asymptomatic hernias.
However, if the hernia is large, painful, or causes other complications, surgery may be necessary. Umbilical hernia surgery is typically performed under general anesthesia and involves closing the opening in the abdominal muscles with sutures or a mesh patch. The surgery is usually performed on an outpatient basis and has a high success rate.
Conclusion
In conclusion, umbilical hernias are a common condition in infants and young children, caused by a congenital weakness in the abdominal muscles. While most umbilical Hernia In Children will close on their own, surgery may be necessary if the hernia is large, painful, or causing other complications. If you suspect that your child may have an umbilical hernia, it is important to seek medical attention to ensure an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment by Paediatric Hernia Specialist in Goregaon Dr. Saurabh Tiwari.
Dr. Saurabh Tiwari
Dr. Saurabh Tiwari (M.B.B.S., M.S., F.M.A.S, M.Ch. Pediatric Surgery) started his surgical career in 2013 after completing his M.B.B.S. from Topiwala National Medical College and B.Y.L. Nair Charitable Hospital, Mumbai. He did his postgraduation in General Surgery from Dr. Panjabrao Deshmukh Memorial Medical College and Hospital, Amravati after which he pursued an M.CH in Pediatric Surgery from Lokmanya Tilak Municipal Medical College and Hospital, Sion, Mumbai under the guidance of Dr. Paras Kothari. He specializes in pediatric, neonatal, and laparoscopic surgeries. He has previously worked at Dr. Babasaheb Ambedkar Hospital, Kandivali. He has also obtained a prestigious fellowship in minimal access surgery (FMAS) from AMASI (Association of minimal access surgeons of India).